The solar cells whether on calculators, satellites or on your roof or even on your wristwatch are also called photovoltaic (PV) cells. Photo meaning “light” and voltaic meaning “electricity”, hence converting sunlight directly into electricity.
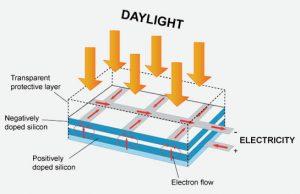
Each of the solar PV panels comprise of a number of solar PV cells. These cells are made up of ultra-thin wafers of silicon, which sit under a transparent protective layer.
When light strikes the cell, a certain portion of it is absorbed within the semiconductor material. This means that the energy of the absorbed light is transferred to the semiconductor. This additional energy knocks electrons loose, allowing them to flow freely. All PV cells also all have one or more electric fields that act to force electrons freed by light absorption to flow in a certain direction. This flow of electrons is a current, and by placing metal contacts on the top and bottom of the PV cell, we can draw on that current for external use. This current, together with the cell’s voltage (which is a result of its built-in electric field or fields), defines the power (or wattage) that the solar cell can produce.
A ”module” is a group of cells connected electrically and packaged into a frame (more commonly known as a solar panel)